When you think of a solar system or a photovoltaic kit, you usually think of photovoltaic panels. However, other elements such as the inverter, cables, connectors, support and monitoring systems (smart meters), protection devices and a possible energy storage system must be added to this component.
In this article, we will explain in detail what a solar inverter is, how it works, the different types, and much more information.

What Is a Solar Inverter?
What is the solar inverter used for? The inverter is considered the heart of a photovoltaic system because it allows all those who install a solar system on their roof to use solar energy inside their homes. The current generated by the solar panels is a direct current (DC) which cannot be used in the home. Therefore, a solar inverter is needed to convert DC into alternating current (AC) so that it can be used daily in our homes.
In addition to performing this important function, the inverter optimizes the production of energy generated by the solar panels to obtain the maximum possible efficiency of the system.
The approximate life span of a PV inverter is around 10 years due to its electronic components, which can be easily replaced. Protecting this device from all possible failures it may encounter is important.
The Main Characteristics of a Solar Inverter
We have seen how these devices play a fundamental role within a solar system. Now let’s see the characteristics of solar inverters.
- As previously mentioned, the main function of a PV inverter is to transform direct current into alternating current to allow its use in our homes
- The inverter optimizes the energy production generated by the efficient solar panels, maximizing system performance
- The solar inverter contains protective devices that allow the system to be protected even in the event of a system failure or short circuit
- The device also performs a surveillance function for the entire system. Thanks to the inverter, we can understand if there are faults in the system or malfunctions in electricity production.
Operation and Installation of Solar Inverters
Once the main tasks performed by this device have been clarified, let’s now see precisely how a solar inverter works.
Solar panels receive sunlight, which is then transformed into electricity. But as we have seen, this electricity is a direct current that cannot be used inside our homes. So how can we use the electricity produced by solar energy? With the solar inverter.
This device is essential for any photovoltaic system and can transform direct current into alternating current. The energy generated by the solar panels is sent directly to the inverter, which carries out this transformation and thus allows us to enjoy the electricity produced by the sun in our homes.
Before installing a solar inverter, the following aspects should be considered:
- The correct functioning of domestic electrical circuits;
- The location of the inverter;
- The electrical connections between the inverter itself and the electrical panel of the house;
For this reason, we advise you to contact professionals in the sector who know how to direct you towards the best choice. We work with over one hundred certified installers ready to help you install your photovoltaic system and resolve all doubts related to the process.
Check out solar panel installation company in Denver to see how much you can save by switching to solar.
The Lights of an Inverter
Each inverter is equipped with 3 different LED indicators (blue, green and red) and together, they are responsible for providing information about the system, such as errors and performance.
Let’s see below their possible combinations and meaning:
- The blue light: indicates that the inverter is communicating with the Monitoring Platform
- The green light: indicates that the system is producing energy
- Flashing green light: Indicates that the system has AC (alternating current) power but is not producing energy
- The red light: Indicates a system error
Types of Solar Inverters
There are two types of solar inverters on the market: single-phase and three-phase.
- Single-phase inverters are used in single-phase networks and have two connectors, one for phase and one for neutral. They are usually used in photovoltaic systems with power below 6 kW.
- On the other hand, three-phase inverters consist of three phases and three different alternating currents. These are products suitable for photovoltaic systems for large companies or industrial warehouses. It is also true that it is possible to find this type of inverter in our homes, but this is an uncommon case.
In addition to this distinction, it is good to distinguish solar inverters for grid-connected systems from inverters for stand-alone photovoltaic systems.
Solar Inverters for Grid-Connected Systems
Solar inverters for systems connected to the electricity grid transform the solar energy generated by the photovoltaic panels into electricity, with the possibility of pouring the surplus energy into the grid and obtaining economic compensation thanks to the Net Metering service.
There are different types of solar inverters. There are four types of grid-connected electric inverters on the market:
- String inverters;
- Centralized inverter;
- Micro inverters;
- Hybrid inverters.
String Inverters
String inverters are the most used and cheapest on the market and require maintenance that does not require additional time and cost. These inverters are usually used for systems not affected by shading, which would limit the optimal use of each string.
For this reason, this type of inverter is perfect for geographical areas where solar radiation remains constant every year, and no solar panels are affected by shade.
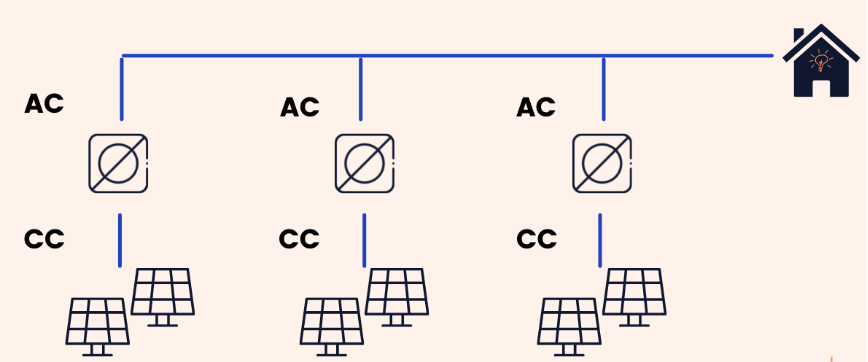
Centralized Inverter
Central inverters are usually used in large photovoltaic systems due to their simple and direct use. The photovoltaic modules are connected in series to form strings up to 1000 V open circuit voltage. In this case, a single inverter is connected to these strings in parallel. Among the negative aspects of this inverter, we mention the impossibility of monitoring each solar panel’s performance and using them in case of shading.
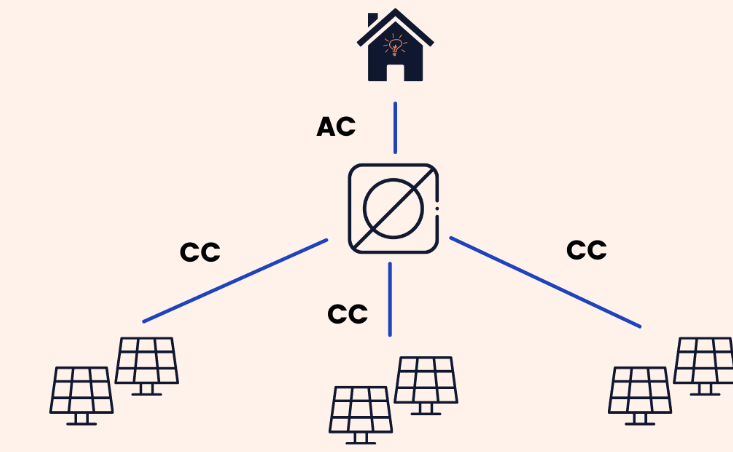
The Micro Inverters
Micro inverters have a different function than string or central inverters, as each device is installed on a single solar panel. This means that every solar module can transform energy into an alternating current. Unlike string inverters, the energy production generated by a panel does not affect the rest, not negatively affecting the performance of the entire photovoltaic system.
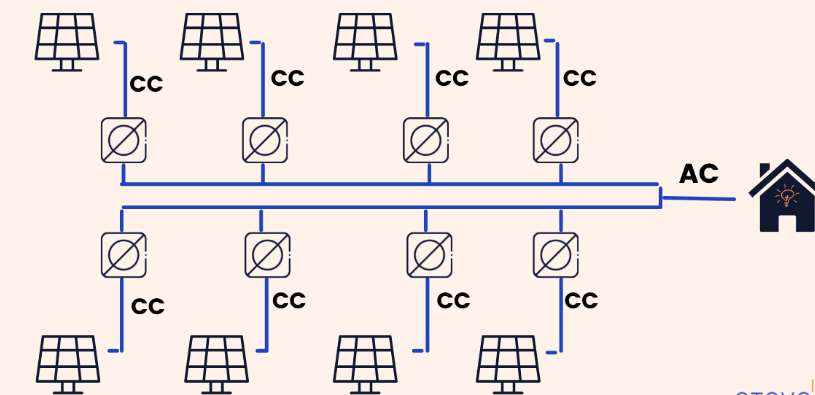
The advantages of micro inverters are:
- The ability to monitor the performance of individual photovoltaic panels
- The ease of expanding the plant
- The low-power dissipation
- The connection of the modules in parallel
- The ease of identifying a faulty module in the event of a failure
- High average life and durability
What’s the downside? The price is higher since these are small inverters built into each panel.
Hybrid Inverter
A hybrid solar inverter has the same function as a conventional string inverter. Still, in addition to transforming energy from panels for domestic use, it ensures the charge/discharge of energy in storage systems.
In addition to the traditional hybrid inverters, there are also the so-called smart inverters on the market: devices capable of charging the photovoltaic batteries with energy from the electricity grid when the price is low and then using it when the photovoltaic system is unable to meet the electricity needs of the house.
This type of technology is designed to obtain the maximum self-sufficiency of the system and allow the maximum possible energy savings. However, it comes at a very high price.
Solar Inverters for Stand-Alone Systems
Stand-alone photovoltaic systems are those not connected to the external electricity grid and require a battery where all the solar energy generated by the photovoltaic modules can be stored. In this case, the inverter connected to this system extracts energy directly from the battery. Then it converts the direct current into alternating current to make it usable at home.
Generally, this type of inverter is used in areas with little or no accessibility to the electrical connection, such as mountain huts or on means of transport, such as campers or boats.

Inverters for off grid solar systems work very similarly to hybrid inverters for grid-connected systems. However, these devices can generate their power grid without relying on the grid.
Solar Inverter: Prices in 2022
As already mentioned, the inverter is a fundamental component of a photovoltaic system. Its price can vary from 300 to 400 euros (micro inverter) to 5000 euros (50 kW three-phase inverter). This price variation depends a lot on the power, quality and type of solar inverter. For example, a 4 kW inverter costs (vat and margin) from 900 to 1200 euros, while the VAT and margin price of a 4 kW hybrid inverter varies from 900 to 1400 euros.
Which Solar Inverter to Choose?
Once we have all the information about our PV system and home, the question always arises: how do I choose the most suitable inverter for my PV system?
Since an inverter costs at least 10% of the system, it is good to identify which is right for us. It is good to understand the power of our system since the power of the inverter will depend a lot on this aspect.
If, for example, we have a 2.5 kW domestic photovoltaic system, we should choose a 3kW power inverter.
Surely, another aspect that must be taken into consideration is also the warranty of the inverter.
- Fronius inverter with 5-year warranty extendable to 10
- Solaredge inverter with a 12-year warranty
- Huawei inverter with a 10-year warranty
- Sma inverter with 5-year warranty extendable to 10
- Zucchetti inverter with a 10-year guarantee
In conclusion, this article explores the world of solar inverters, which are very important for the operation of a solar system.
Frequent Questions
What Is the Inverter Used for in a Photovoltaic System?
The solar inverter is the heart of a photovoltaic system since it transforms the direct current produced by the solar panels into alternating current. This is then fed into the domestic electricity grid to be used inside our homes.
How Do You Choose the Power of a Solar Inverter?
The power of the inverter must be chosen on the basis of the sum of the powers of the 220V users we want to feed simultaneously.