Are you struggling to effectively store and manage the vast amount of unstructured data in your organization? Look no further than data lakes. Data lakes have emerged as a powerful solution for storing big data, providing numerous advantages and addressing various challenges associated with unstructured data.
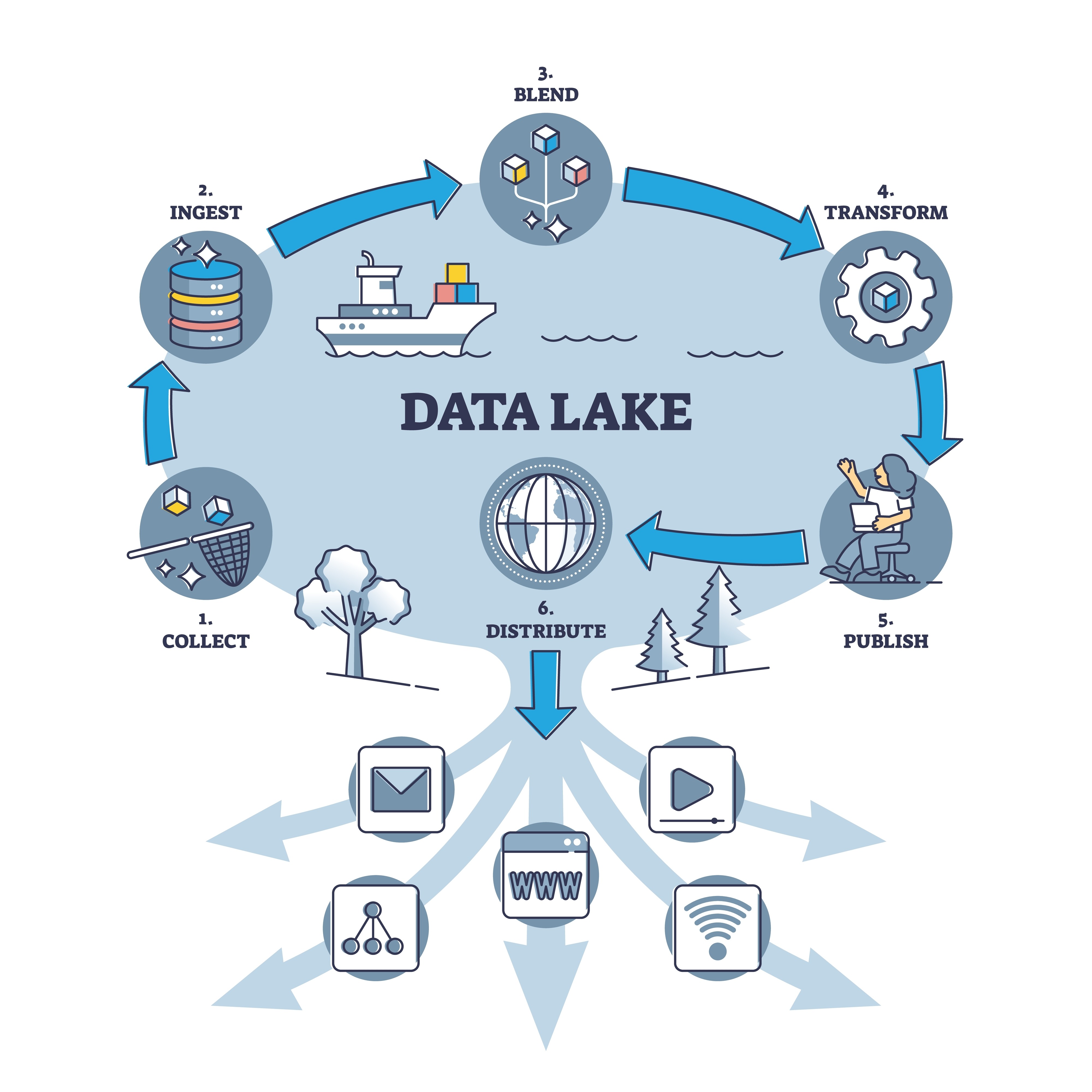
In today’s fast-paced digital world, flexibility is key when it comes to data storage. With a data lake, you can easily store diverse types of unstructured data, such as text files, images, audio files, and videos. This flexibility allows you to consolidate all your raw data into one centralized repository, eliminating the need for multiple siloed systems. By having all your unstructured data in one place, you gain a holistic view of your information and can perform comprehensive analysis and insights that were previously not possible. Plus, with the ability to quickly and easily access any type of unstructured data from a single location, you can streamline your processes and improve efficiency across your organization. So why struggle with scattered storage solutions when a data lake offers such convenience?
Flexibility in Data Storage
Data lakes offer the incredible advantage of storing unstructured data, providing businesses with the flexibility they need to efficiently manage and analyze vast amounts of information. With traditional data storage systems, structured data is typically organized in a predetermined format, making it difficult to incorporate new types of data orchestration tools and adapt to changing business needs. However, data lakes are designed to accommodate any type of data, regardless of its structure or origin.
This flexibility allows businesses to store a wide range of unstructured data sources, such as social media posts, sensor readings, logs, and multimedia content. By storing all this unstructured data in a single repository, companies can avoid the time-consuming process of transforming and restructuring the data before analysis. Instead, they can focus on extracting valuable insights from these diverse sources of information. The ability to quickly ingest and store large volumes of unstructured data also enables businesses to capture real-time updates and make more informed decisions based on up-to-date information. Overall, this flexibility in data storage empowers organizations to harness the full potential of their big data assets and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Handling Diverse Types of Data
When dealing with a wide range of information, it’s crucial to find effective ways to manage and make sense of various types of data in data lakes. With the vast amount of unstructured data being stored in data lakes, it becomes essential to have mechanisms in place that can handle diverse types of data seamlessly. Data lakes allow for the storage of not only structured and semi-structured data but also unstructured data such as text documents, images, videos, and social media posts.
One advantage of using a data lake for handling diverse types of data is the ability to store everything in its raw format. Unlike traditional databases that require predefined schemas, a data lake allows for the ingestion and storage of different types of unstructured data without any transformation or normalization. This flexibility enables organizations to capture and analyze large volumes of diverse sources without worrying about upfront schema design limitations. Additionally, by keeping the original format intact, businesses can preserve valuable context and metadata associated with each type of data.
However, handling diverse types of unstructured data also presents challenges when it comes to organizing and retrieving information effectively. Without proper metadata management strategies in place, finding specific pieces of information within a massive pool can become time-consuming and inefficient. It’s important for organizations to implement robust metadata frameworks that capture relevant information about each piece of unstructured data stored in the lake. This way, users can easily search for and retrieve specific files or objects based on criteria such as file type, creation date, source system, or any other relevant attribute associated with the dataset.
Scalability for Big Data
Scalability is a crucial factor to consider when managing and analyzing large volumes of diverse information in order to ensure efficient processing. As your data lake grows, it becomes imperative to have a scalable infrastructure that can handle the increasing demands of big data. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Elasticity: A scalable data lake should be able to expand or contract as per the requirements. It should allow you to easily add or remove resources based on the workload, ensuring optimal performance at all times.
- Distributed Processing: With scalability comes the need for distributed processing capabilities. Your data lake should be able to distribute the workload across multiple nodes or clusters, allowing for parallel processing and faster analysis of big data.
- Fault Tolerance: As your data lake expands, there’s a higher chance of encountering hardware failures or network issues. A scalable solution should have built-in fault tolerance mechanisms such as replication and redundancy, ensuring that your data remains safe and accessible even in case of failures.
- Resource Optimization: Scalability doesn’t just mean adding more resources; it also involves optimizing their utilization. A good data lake should be able to efficiently utilize available resources by automatically adjusting resource allocation based on demand.
By considering these factors, you can ensure that your data lake is capable of scaling seamlessly with growing volumes of unstructured data, allowing for efficient storage and analysis of big data.
Challenges in Data Quality
To truly harness the power of your expanding information ecosystem, you need to confront the formidable obstacles that stand in the way of ensuring high-quality data. One of the main challenges in data quality when dealing with unstructured data in a data lake is the lack of predefined structure and organization. Unlike structured data, unstructured data does not have a pre-defined schema or format, making it difficult to validate its accuracy and completeness. This can lead to issues such as missing or duplicate records, inconsistent formatting, and unreliable metadata.
Another challenge in ensuring data quality in a data lake is the sheer volume of unstructured data. Data lakes are designed to store vast amounts of raw and unfiltered data, which can result in information overload. It becomes challenging to identify relevant and reliable sources amidst this sea of unstructured information. Additionally, as more and more disparate sources contribute to the data lake, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain consistency and ensure that all incoming data adheres to quality standards.
Addressing these challenges requires implementing robust processes for cleansing, validating, and transforming unstructured data into usable formats. This involves techniques such as natural language processing (NLP) for extracting meaningful insights from textual content and machine learning algorithms for identifying patterns and anomalies within the dataset. By investing time and resources into improving the quality of your unstructured data within a data lake, you can unlock its true potential for informed decision-making and gaining valuable business insights.
Security and Governance Concerns
Ensure that you thoroughly understand the crucial concerns surrounding security and governance in order to effectively protect your valuable information assets in a data lake. When it comes to security, one of the main challenges is ensuring that unauthorized individuals do not gain access to sensitive data stored in the data lake. This can be achieved through implementing strong authentication measures, such as multi factor authentication and encryption techniques. Additionally, regular monitoring and auditing of access logs can help identify any suspicious activity and prevent potential breaches.
Governance is another important aspect to consider when managing a data lake. It involves defining policies and procedures for data management, ensuring compliance with regulations and industry standards, as well as establishing roles and responsibilities for data stewards. By implementing proper governance practices, you can maintain data quality, ensure consistency across different datasets, and enable efficient collaboration among various teams within your organization. It is also crucial to establish clear guidelines for data usage and ensure that all users are aware of their responsibilities when accessing or manipulating the data within the lake. By addressing these security and governance concerns adequately, you can maximize the value of your unstructured data while minimizing risks associated with its storage in a data lake.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data lakes offer numerous advantages for storing unstructured data. They provide flexibility in data storage, allowing organizations to store and analyze diverse types of data without the need for upfront schema design. This flexibility enables businesses to adapt and evolve their data analysis strategies as needed.
Additionally, data lakes offer scalability for big data. With the ability to store vast amounts of information, organizations can easily scale their storage capacity as their data grows. This ensures that businesses can effectively manage and analyze large volumes of unstructured data without facing limitations.
However, it is important to acknowledge the challenges that come with using data lakes. Data quality can be a significant concern, as unstructured data may contain errors or inconsistencies that need to be addressed before analysis. Furthermore, security and governance must be carefully managed to protect sensitive information stored in the lake.
Overall, while there are challenges associated with storing unstructured data in a lake, the benefits outweigh them. By leveraging the flexibility and scalability offered by these storage systems, organizations can unlock valuable insights from their unstructured datasets and gain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.