Smart lights have emerged as a revolutionary technology, transforming the way we interact with and control our lighting systems. These innovative devices offer more than just illumination; they provide customizable experiences, energy efficiency, and the convenience of remote control.
Types of smart lights, including bulbs, strips, and fixtures, each offering unique features for customizable and convenient lighting experiences. In this guide, we’ll explore the basics of smart lights, shedding light on how they work, their features, and the benefits they bring to modern living.
1. What Are Smart Lights?
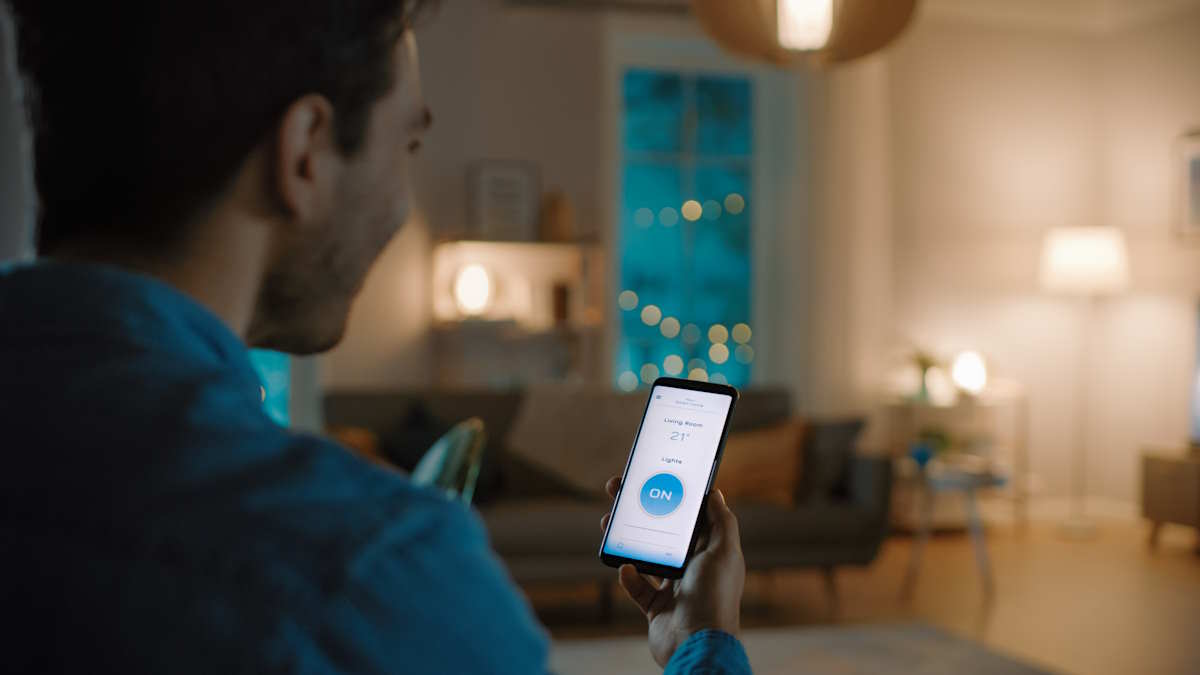
Smart lights are lighting fixtures equipped with wireless connectivity and smart technology, allowing users to control them remotely using smartphones, tablets, voice commands, or dedicated smart home platforms. Unlike traditional lighting, smart lights offer a wide range of features beyond simple on/off functionality.
2. Key Components of Smart Lights:
– LED Technology: Smart lights primarily use LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology, offering energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and the ability to produce various colors and intensities.
– Wireless Connectivity: Smart lights communicate wirelessly through protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave. This enables seamless integration into smart home ecosystems.
– Smart Controllers: These lights are paired with smart controllers, which can be physical devices, smartphone apps, voice assistants, or central smart home hubs.
– Color and Intensity Adjustability: A defining feature of smart lights is the ability to change color temperatures and adjust brightness levels. This customization allows users to create different atmospheres for various occasions.
3. How Do Smart Lights Work?
– Connectivity: Smart lights connect to a home network through the chosen wireless protocol. This connection enables communication between the lights and other smart devices within the home.
– Control Platforms: Users can control smart lights using dedicated apps on smartphones or tablets. Many smart lights also integrate with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit, allowing users to control lights using voice commands.
– Automation: Smart lights can be integrated into automation scenarios. For example, lights can automatically turn on at sunset or change colors based on the time of day.
4. Features and Functionalities:
– Color Changing: Smart lights can produce a spectrum of colors, allowing users to create dynamic and customizable lighting scenes. This feature is particularly popular for setting moods or enhancing entertainment experiences.
– Dimming Capabilities: Adjusting the brightness of smart lights provides flexibility in creating the desired ambiance for different activities, from movie nights to reading sessions.
– Scheduling: Users can schedule smart lights to turn on or off at specific times. This feature enhances energy efficiency and can simulate occupancy when users are away from home.
– Remote Control: Whether at home or away, users can control their smart lights remotely using smartphone apps. This feature adds convenience and security.
5. Installation and Compatibility:
– Installation: Smart lights are designed for easy installation, often replacing traditional light bulbs or fixtures. Some may require additional smart switches or hubs for full functionality.
– Compatibility: Before purchasing smart lights, users should ensure compatibility with their existing smart home ecosystem. Many smart lights work seamlessly with popular platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple HomeKit.

6. Benefits of Smart Lights:
– Energy Efficiency: Smart lights use LED technology and offer energy-saving features like scheduling and motion sensing, contributing to reduced energy consumption.
– Customization: The ability to customize color, brightness, and scheduling provides users with personalized lighting experiences to suit their preferences.
– Convenience: Remote control, voice commands, and automation add convenience to daily life. Users can adjust lighting without leaving their seats or even when they are away from home.
– Security: Smart lights can be programmed to simulate occupancy, deterring potential intruders when homeowners are away.
– Longevity: LED technology in smart lights ensures a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, reducing the frequency of replacements.
7. Challenges and Considerations:
– Cost: Smart lights may have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional lighting options. However, long-term energy savings and added functionalities often justify the initial investment.
– Compatibility Issues: Users should ensure that their chosen smart lights are compatible with their existing smart home devices and platforms.
– Privacy Concerns: As with any connected device, users should be mindful of privacy and security. Regular software updates and secure network practices help mitigate potential risks.
Conclusion:
Smart lights represent a significant evolution in lighting technology, offering a blend of functionality, aesthetics, and energy efficiency. The ability to control lighting with precision, create customized atmospheres, and integrate with broader smart home ecosystems has made them a popular choice for modern homeowners. As technology continues to advance, smart lights will likely play a crucial role in shaping the future of home lighting, providing users with enhanced experiences and greater control over their living spaces.